CASIMIR EFFECT M. MOHIDEEN, V.M. Unique to the Casimir force is its strong dependence on. The Casimir effect from a condensed matter perspective. The Casimir effect from a condensed matter. “ The Casimir effect: A force from nothing. The casimir effect: a force from nothing, physics world september 2002. Garrison Managerial Accounting 14e Solutions Pdf Polaris Jet Ski Service Manuals Download.
Casimir forces on parallel plates The typical example is of the two conductive plates in a, placed a few nanometers apart. In a description, the lack of an external field means that there is no field between the plates, and no force would be measured between them. When this field is instead studied using the, it is seen that the plates do affect the which constitute the field, and generate a net force – either an attraction or a repulsion depending on the specific arrangement of the two plates. Although the Casimir effect can be expressed in terms of interacting with the objects, it is best described and more easily calculated in terms of the of a in the intervening space between the objects. This force has been measured and is a striking example of an effect captured formally.
The treatment of boundary conditions in these calculations has led to some controversy. In fact, 'Casimir's original goal was to compute the between ' of the conductive plates. Thus it can be interpreted without any reference to the zero-point energy (vacuum energy) of quantum fields. Because the strength of the force falls off rapidly with distance, it is measurable only when the distance between the objects is extremely small. On a submicron scale, this force becomes so strong that it becomes the dominant force between uncharged conductors.
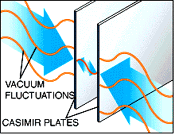


In fact, at separations of 10 nm – about 100 times the typical size of an atom – the Casimir effect produces the equivalent of about 1 (the precise value depending on surface geometry and other factors). A water wave analogue of the Casimir effect. Two parallel plates are submerged into colored water contained in a.
When the sonicator is turned on, waves are excited imitating vacuum fluctuations; as a result, the plates are forced together. Any medium supporting oscillations has an analogue of the Casimir effect.
For example, beads on a string as well as plates submerged in noisy water or gas illustrate the Casimir force. In modern, the Casimir effect plays an important role in the of the; in, it is significant in some aspects of emerging and. History physicists Hendrik Casimir and at proposed the existence of a force between two polarizable atoms and between such an atom and a conducting plate in 1947, this special form is called the Casimir–Polder force.
Renormalization
After a conversation with, who suggested it had something to do with zero-point energy, Casimir alone formulated the theory predicting a force between neutral conducting plates in 1948 which is called the Casimir effect in the narrow sense. Predictions of the force were later extended to finite-conductivity metals and dielectrics, and recent calculations have considered more general geometries.
Experiments before 1997 had observed the force qualitatively, and indirect validation of the predicted Casimir energy had been made by measuring the thickness of films. However it was not until 1997 that a direct experiment by S. Lamoreaux quantitatively measured the force to within 15% of the value predicted by the theory.
V M Mostepanenko
Subsequent experiments approach an accuracy of a few percent. Possible causes Vacuum energy.